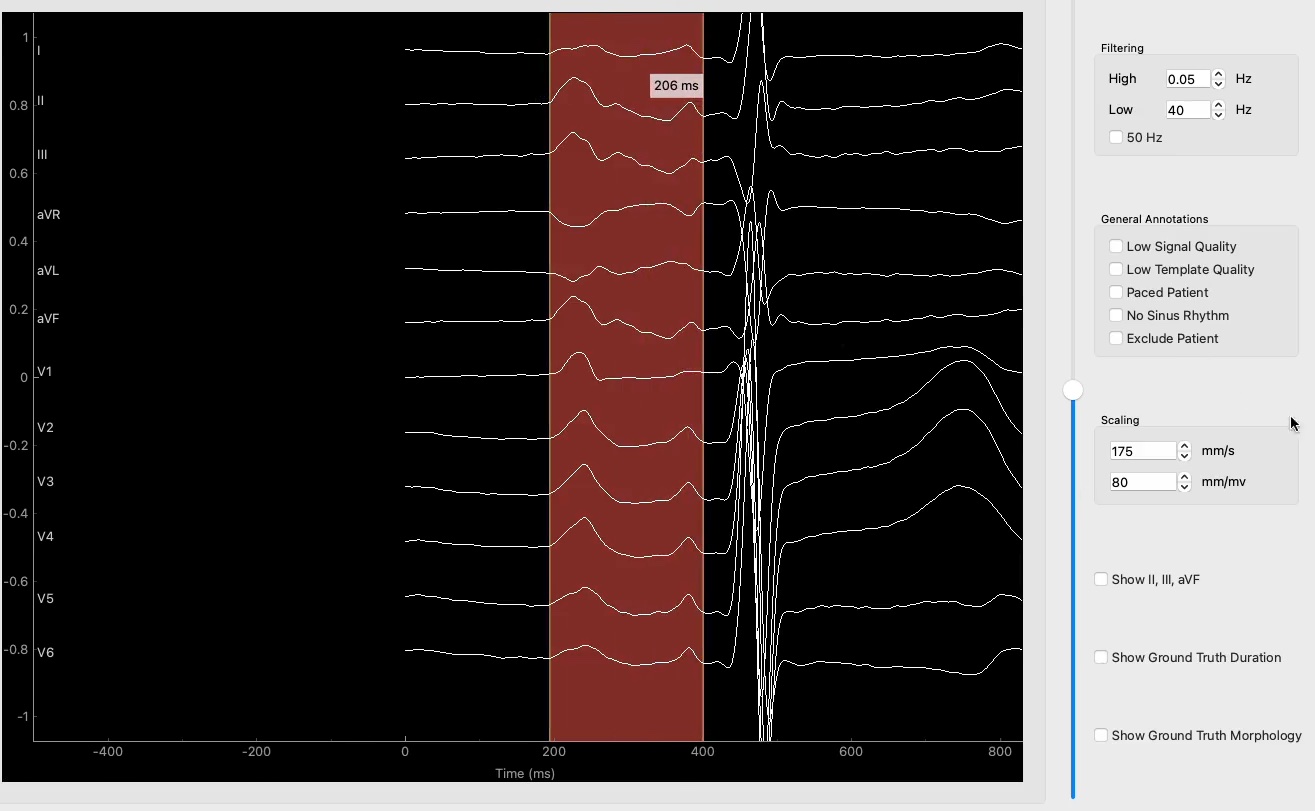
 Atrial cardiomyopathy (AtCM) is associated with slow-conducting low-voltage areas and therefore prolonged total atrial conduction time. Jadidi et al. demonstrated that total atrial conduction time correlates with amplified P-wave duration (APWD). Furthermore, APW morphology has been demonstrated to assist in staging AtCM. These findings suggest that APW duration and morphology measured in a 12-lead-ECG enables the non-invasive diagnosis of AtCM.
Atrial cardiomyopathy (AtCM) is associated with slow-conducting low-voltage areas and therefore prolonged total atrial conduction time. Jadidi et al. demonstrated that total atrial conduction time correlates with amplified P-wave duration (APWD). Furthermore, APW morphology has been demonstrated to assist in staging AtCM. These findings suggest that APW duration and morphology measured in a 12-lead-ECG enables the non-invasive diagnosis of AtCM.
Despite its diagnostic value, manual annotation of APWD is time-consuming, subjective, and not scalable, rendering it impractical for large-scale screening or retrospective cohort studies. To overcome these limitations, we aim to develop an automated, AI-based algorithm that can annotate APWD reliably and reproducibly. A critical prerequisite for this is the availability of high-quality expertlabeled ECG data, which will serve as training and validation data for the algorithm.
 Atrial cardiomyopathy (AtCM) is associated with slow-conducting low-voltage areas and therefore prolonged total atrial conduction time. Jadidi et al. demonstrated that total atrial conduction time correlates with amplified P-wave duration (APWD). Furthermore, APW morphology has been demonstrated to assist in staging AtCM. These findings suggest that APW duration and morphology measured in a 12-lead-ECG enables the non-invasive diagnosis of AtCM.
Atrial cardiomyopathy (AtCM) is associated with slow-conducting low-voltage areas and therefore prolonged total atrial conduction time. Jadidi et al. demonstrated that total atrial conduction time correlates with amplified P-wave duration (APWD). Furthermore, APW morphology has been demonstrated to assist in staging AtCM. These findings suggest that APW duration and morphology measured in a 12-lead-ECG enables the non-invasive diagnosis of AtCM.
