In silico characterization of pace-and-drive capacity of the human sinus node effects of cellular variability and tissue structure
- type:Bachelor or master thesis
- tutor:
Motivation and Background
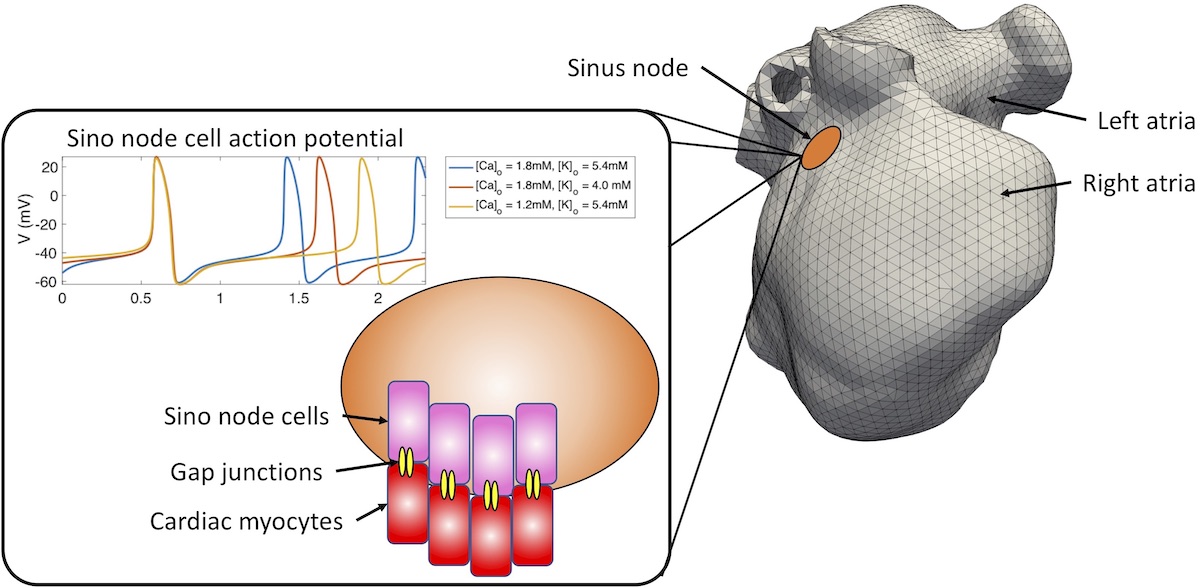
Computational models of cardiac electrophysiology have significantly advanced in the last years and nowadays contribute to understanding fundamental physiological and disease mechanisms, optimization of diagnostic tools, and tailored therapeutic approaches. Most computational models of cardiac electrophysiology use external impulses to initiate excitation waves. Under healthy conditions, this approach is valid if only the spread of excitation waves within the working myocardium is of interest. However, the heart possesses the sinus node as its primary intrinsic pacemaker composed of cells that rhythmically generate impulses themselves. Understanding the fundamental mechanisms by which cardiac depolarization waves are initiated in the sinus node and excite the surrounding atrial tissue is of paramount importance under many pathological conditions (e.g., the frequent case of change of ion concentrations in kidney disease patients).
Project
The student will develop multiscale computational simulations to understand the coupling between the sinus node cells and the cardiac tissue that leads to successful pace-and-drive behavior.
Skills
Good programming skills (Matlab/Python)
Ability to work independently
Commitment and self-organization skills
Communication and work will be done in English
Start date
April/May 2021
For more information feel free to send an email or just drop by my office.
