3D COMSOL Simulations of Pulsed Field Ablation in the Cardiac Autonomic Nervous System
- chair:Computational Cardiac Modeling
- type:Bachelor or Master Thesis
- tutor:
Motivation
Pulsed field ablation (PFA) is a novel, non-thermal ablation method that selectively targets cardiac tissue through electroporation-creating pores in cell membranes by applying high-intensity electric fields. This approach offers promising advantages over traditional thermal ablation, including enhanced precision, reduced collateral damage, and improved safety profiles. Another potential use case for PFA is targeting of ganglionated plexi, which play an important role in the development of AF through the disregulation of the autonomic nervous system. Previous computational studies investigated epicardial PFA targeting ganglionated plexi (GP) embedded within epicardial adipose tissue (EAT) layers. This prior work demonstrated that. while PFA effectively ablates superficial GPs, deeper targets remain challenging due to electric field attenuation. You will contribute to the refinement and optimization of PFA protocols, aiming to enhance therapeutic outcomes for atrial fibrillation treatment.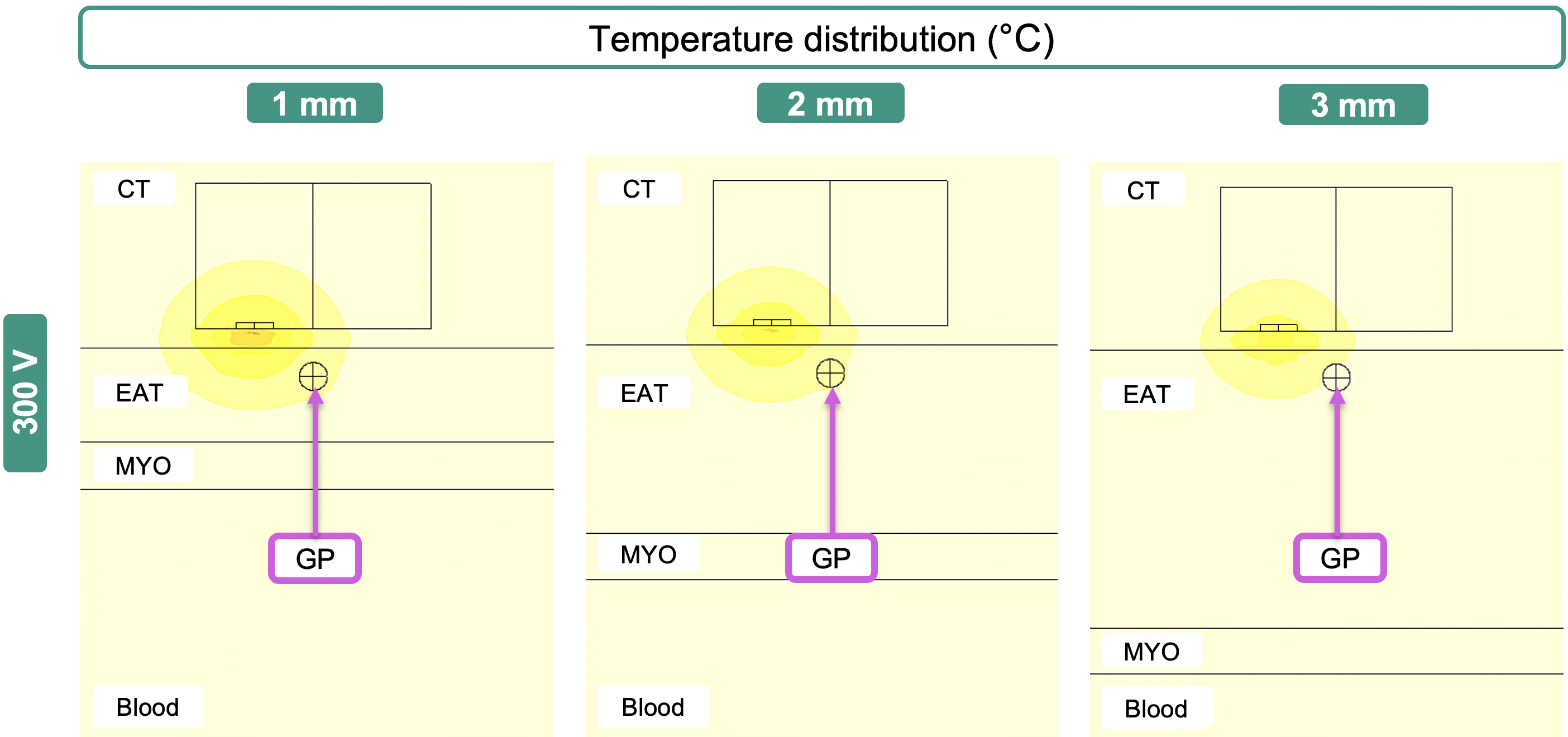
Student Project
The student will extend existing 3D time-dependent COMSOL simulations of epicardial PFA to optimize GP ablation across variable anatomical conditions. Key tasks include incorporating cardiac tissue anisotropy, simulating dynamic effects such as cardiac motion, and performing parameter sensitivity analyses. The student will also investigate the combined impact of anatomical factors—like EAT thickness and ganglion depth—on electric field distribution and ablation efficacy, while exploring electrode configurations and pulse settings to enhance field uniformity and selectivity without exceeding thermal damage limits.Skills needed
Written and spoken English
Experience in COMSOL and Python desirable not mandatory

